Back
Abstract: Poster/Statement:
Patients undergoing this surgical procedure have been shown to have moderate to severe postoperative pain.
Zynrelef (HTX-011) is an extended-release, dual-acting local anesthetic (DALA) formulation comprising bupivacaine and low-dose meloxicam in a controlled-diffusion polymer that allows for controlled delivery of active ingredients over 72 hours.
HTX-011 has demonstrated superior postoperative pain management and limited opioid use compared with the standard-of-care local anesthetic bupivacaine hydrochloride (HCL) and saline placed in randomized, controlled registration studies of patients undergoing bunionectomy, herniorrhaphy, and TKA (total knee arthroplasty).
The objective of this case series was to evaluate the novel use of Zynrelef (HTX-011) in patients undergoing oral and dental surgery and evaluate their concomitant use of opioid analgesics.
Methods of Data Analysis:
This analysis examined the effect of HTX-011 on the treatment of postoperative pain and opioid consumption following multiple extractions and implants placed in single- and dual-arch oral surgery.
Sample size: The study included patients who underwent 10 patients
Duration: 07/2021 through 05/15/2022
Statistical model- N/A in this case series due to “n” and accepting of all patients.
Subjective Analysis: provided
Selection:
Patients who are undergoing multiple dental extractions, with or without gum grafting, multiple implant placement; single or dual arch treatments with bone reduction, and subsequent placement of dental prosthetic or denture between July 2021 and May 2022.
A series of 10 patients were selected and enrolled sequentially. No patients were excluded from selection.
All patients were risk stratified utilizing the ASA Physical Status process and were ranged from ASA 1 through ASA 3 patients.
Patient ages ranged in age from 29 to 70 and received deep sedation for their anesthetic.
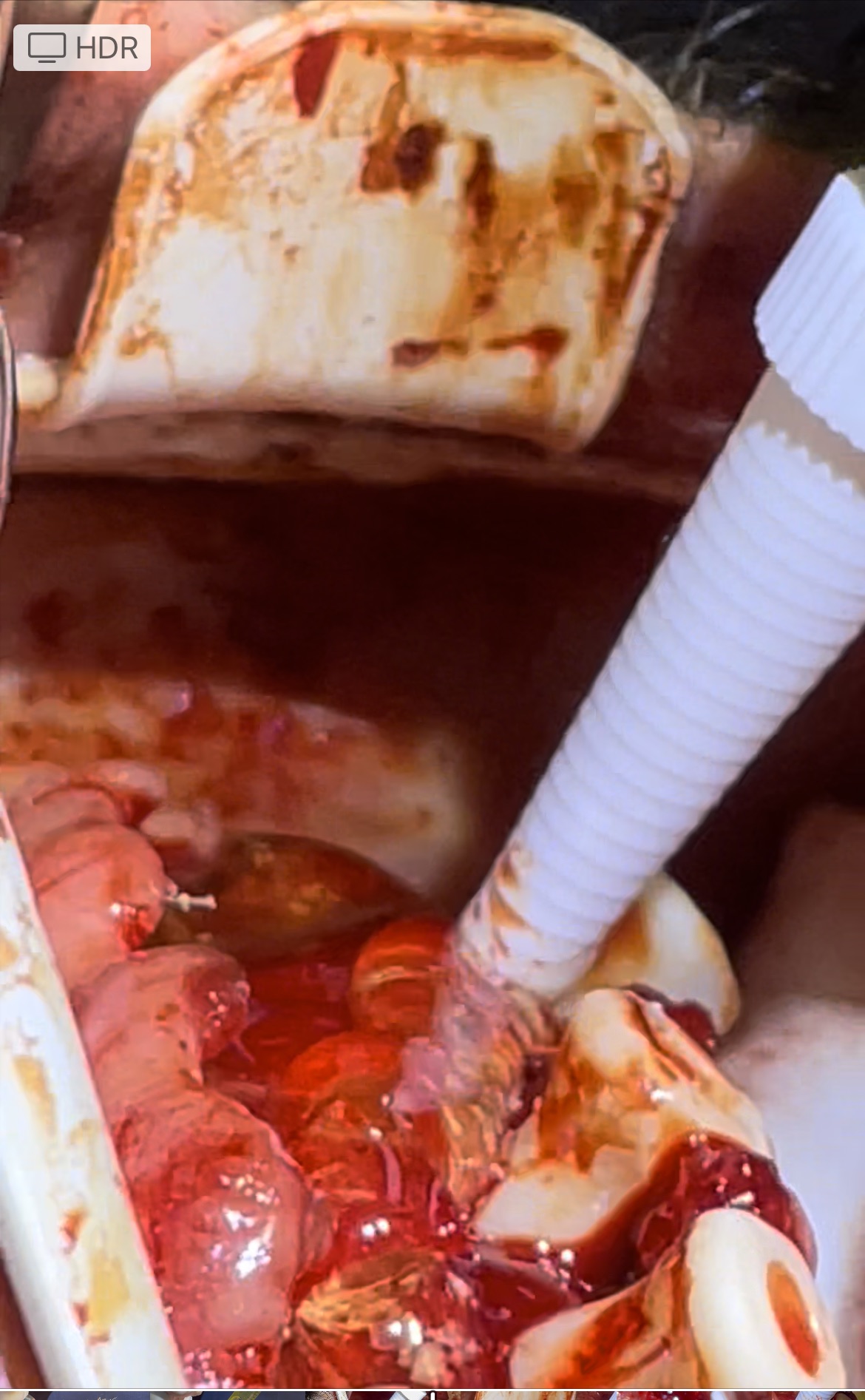
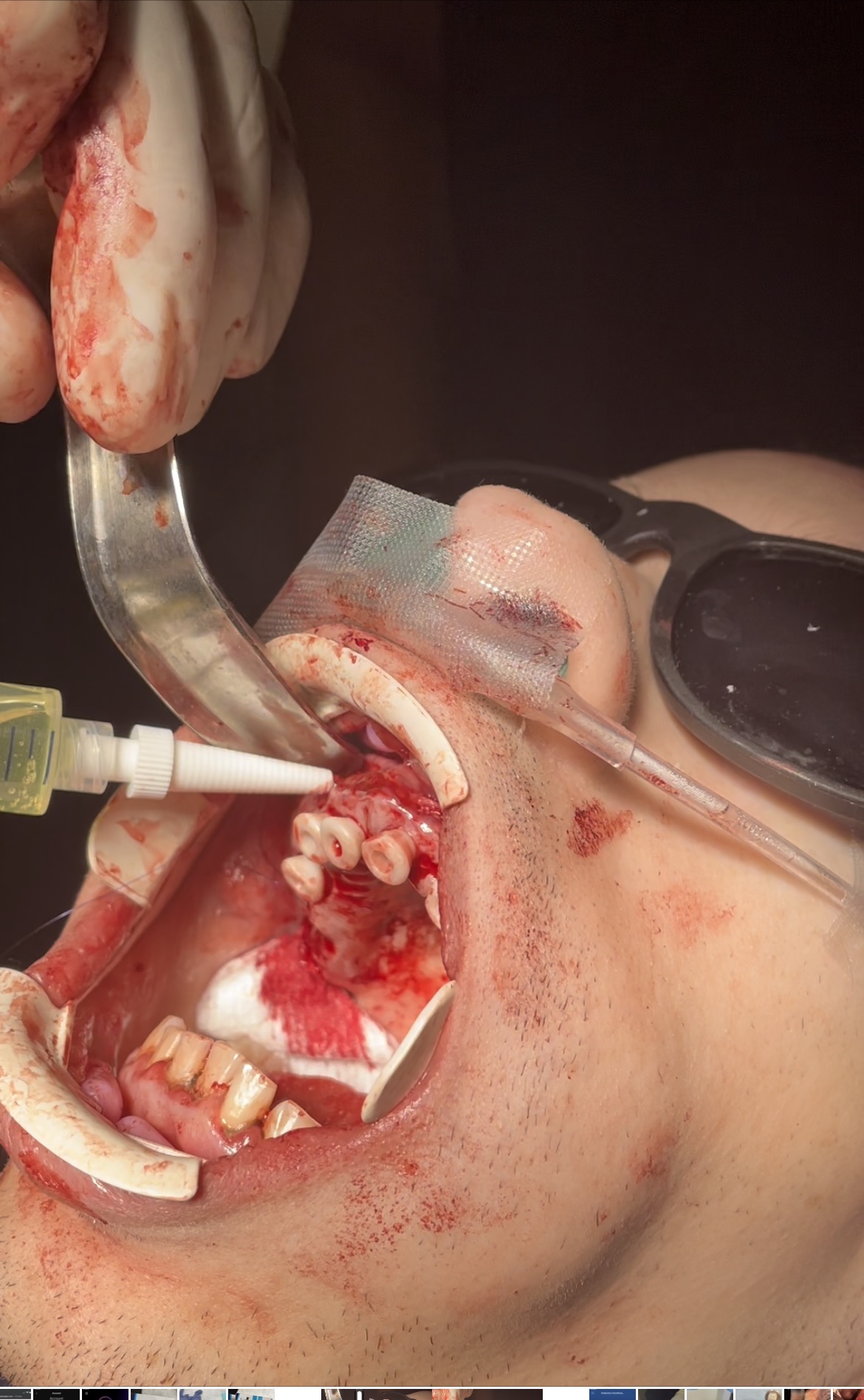
Zynrelef (HTX-011) was administered to patients by the operating provider. Prior to closure of each arch, a total of 1.5 to 2.5mls of HTX-011 was applied along the gumline and surgical flap. This was applied directly to the wound site. For patients who only had 1 arch completed, Zynrelef was only applied to that operative site.
Results:
All patients had successful perioperative courses and surgical engagements.
No patients had any postoperative wound infections per information provided.
All patients received a prescription of postoperative opioid analgesics.
All patients received followup calls from the surgical providers, office consistent with their treatment protocols.
Patients on followup were asked about their postoperative course and information as they related to their pain.
Based on current findings, 7 of the 10 patients avoided the use of opioids postoperatively.
One patient (10%) used a small amount of opioids “out of fear” and not actual pain, and then they realized they didn’t “need it” and stopped.
The remaining 20% of patients did use the opioids, and 2 of the 3 who initially took them and continued were individuals who also persisted smoking postoperatively.
Outcomes:
Please note the outcomes data were subjective in nature but provides a strong foundation in which to base some relevant conclusions.
Conclusions:
Over the last number of years, patients have sought care for their carious teeth, periodontal disease, and a desire to have a healthier lifestyle. These patients are receiving this care in a number of different practice settings. They are turning to complex surgical treatments that include “teeth in a day."
These findings show a dramatic response to this treatment regimen of utilizing Zynrelef (HTX-011). Seven out of 10 patients reported to not using opioids postoperatively. This finding is quite relevant given society’s challenges with opioid use. There will need to be additional studies to substantiate these findings, but there is a compelling reason to consider the adjunctive use of HTX-011 in this patient population.
Anesthesia
(1) HTX-011 (Zynrelef) for Treatment of Postop Pain for Multiple Extractions and Implants in Single and Dual Arch Surgeries: A Case Series.
Thursday, September 15, 2022
1:30 PM – 3:00 PM CDT
Application of Zynrelef (1)

Application of HTX-011


Stanford Plavin, MD- Board Certified Anesthesiologist
Founding Member
Oral Surgery Anesthesia Associates
Atlanta, Georgia, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Disclosure(s):
Stanford Plavin, MD- Board Certified Anesthesiologist: No relevant disclosure to display
Patients undergoing this surgical procedure have been shown to have moderate to severe postoperative pain.
Zynrelef (HTX-011) is an extended-release, dual-acting local anesthetic (DALA) formulation comprising bupivacaine and low-dose meloxicam in a controlled-diffusion polymer that allows for controlled delivery of active ingredients over 72 hours.
HTX-011 has demonstrated superior postoperative pain management and limited opioid use compared with the standard-of-care local anesthetic bupivacaine hydrochloride (HCL) and saline placed in randomized, controlled registration studies of patients undergoing bunionectomy, herniorrhaphy, and TKA (total knee arthroplasty).
The objective of this case series was to evaluate the novel use of Zynrelef (HTX-011) in patients undergoing oral and dental surgery and evaluate their concomitant use of opioid analgesics.
Methods of Data Analysis:
This analysis examined the effect of HTX-011 on the treatment of postoperative pain and opioid consumption following multiple extractions and implants placed in single- and dual-arch oral surgery.
Sample size: The study included patients who underwent 10 patients
Duration: 07/2021 through 05/15/2022
Statistical model- N/A in this case series due to “n” and accepting of all patients.
Subjective Analysis: provided
Selection:
Patients who are undergoing multiple dental extractions, with or without gum grafting, multiple implant placement; single or dual arch treatments with bone reduction, and subsequent placement of dental prosthetic or denture between July 2021 and May 2022.
A series of 10 patients were selected and enrolled sequentially. No patients were excluded from selection.
All patients were risk stratified utilizing the ASA Physical Status process and were ranged from ASA 1 through ASA 3 patients.
Patient ages ranged in age from 29 to 70 and received deep sedation for their anesthetic.
Zynrelef (HTX-011) was administered to patients by the operating provider. Prior to closure of each arch, a total of 1.5 to 2.5mls of HTX-011 was applied along the gumline and surgical flap. This was applied directly to the wound site. For patients who only had 1 arch completed, Zynrelef was only applied to that operative site.
Results:
All patients had successful perioperative courses and surgical engagements.
No patients had any postoperative wound infections per information provided.
All patients received a prescription of postoperative opioid analgesics.
All patients received followup calls from the surgical providers, office consistent with their treatment protocols.
Patients on followup were asked about their postoperative course and information as they related to their pain.
Based on current findings, 7 of the 10 patients avoided the use of opioids postoperatively.
One patient (10%) used a small amount of opioids “out of fear” and not actual pain, and then they realized they didn’t “need it” and stopped.
The remaining 20% of patients did use the opioids, and 2 of the 3 who initially took them and continued were individuals who also persisted smoking postoperatively.
Outcomes:
Please note the outcomes data were subjective in nature but provides a strong foundation in which to base some relevant conclusions.
Conclusions:
Over the last number of years, patients have sought care for their carious teeth, periodontal disease, and a desire to have a healthier lifestyle. These patients are receiving this care in a number of different practice settings. They are turning to complex surgical treatments that include “teeth in a day."
These findings show a dramatic response to this treatment regimen of utilizing Zynrelef (HTX-011). Seven out of 10 patients reported to not using opioids postoperatively. This finding is quite relevant given society’s challenges with opioid use. There will need to be additional studies to substantiate these findings, but there is a compelling reason to consider the adjunctive use of HTX-011 in this patient population.
