Category: Infections in Immunocompromised Individuals
Poster Session: Infections in Immunocompromised Individuals
1105 - The Burden of Infections Prior to Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) Modified T-cell Therapy Predicts Post-CAR T-cell Infectious Complications
- WG
Will Garner
Infectious Diseases Fellow
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- PS
Palash Samanta
Dr
UPMC
Pittsburgh, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- KD
Kathleen Dorritie
Assistant Professor of Medicine
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, University of Pittsburgh, Hillman Cancer Center
Pittsburgh, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- AS
Alison Sehgal
Assistant Professor of Medicine
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, University of Pittsburgh, Hillman Cancer Center
Pittsburgh, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- DW
Denise Winfield
Nurse Practitioner
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Hillman Cancer Center
Pittsburgh, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- MA
Mounzer Agha
Director of the Mario Lemieux Center for Blood Cancers, Associate Professor of Medicine
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, University of Pittsburgh, Hillman Cancer Center
Pittsburgh, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- RB
Robert Boudreau
Core Director for Biostatistics, Center for Aging and Population Health, Assistant Professor
University of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- MN
M. Hong T. Nguyen
Professorof Medicine
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
Pittsburgh, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.

Ghady Haidar
Assistant Professor of Medicine
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
Pittsburgh, PADisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Background:
CAR T -cell therapy (CTT) is a novel treatment for B-cell cancers. CTT patients (pt) are at risk of infection due to neutropenia, cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and CAR T-cell related encephalopathy syndrome (CRES), which are treated with steroids and tocilizumab (anti-IL-6). This is a single-center study evaluating the risk factors for infection after CTT.
Methods:
A retrospective review was conducted of 60 consecutive CTT recipients between 7/17/17 and 9/5/19. Data was collected from 6 months (mo) pre- and at least 6 mo post-CTT. Data was censored for death, additional chemotherapy, or loss to follow up. Cox proportional hazard and Poisson regression were used.
Results:
Median age was 66 (23-84) years; 48% (29) were female. The most common cancer was non-Hodgkin lymphoma (89%, 54). 25% (15) had a prior stem cell transplant (SCT). 73% (44) and 45% (27) of pts developed CRS and CRES, respectively. 43% (26) received steroids; 65% (39) received tocilizumab. In the 6 mo pre-CTT, 39 infections occurred in 45% (27) of pts. 103 infections occurred in 66% (40) after CTT; 33 (55%) had an infection within 6 mo. Infections were bacterial (52%; 54/103), viral (30%; 37/103), fungal (10%; 10/103), mycobacterial (1%; 1/103), protozoal (1%; 1/103). Cumulative incidence of infection in the first 6 mo are shown in Fig 1. All-cause and infection-related mortality were 32% (19) and 15% (9), respectively. Mortality among pts with fungal infections was 20% (2/10). Infection density was 1.28 and 0.58 infections per 100 pt-days between days 0-30 and 30-89, respectively. Factors associated with infection post CTT were number (no.) of infections in the 6 mo prior to infusion (HR 1.62, CI [1.1-2.38]; p=0.015), no. of lines of therapy in the 6 mo pre-CTT (HR 1.52, CI [1.01-2.27]; p=0.04), prior allogeneic SCT (HR 5.96, CI [1.34-26.47]; p=0.019), and no. of tocilizumab doses. Grade 1 CRS and grade 2 CRES were risk factors between days 0-30 and 0-180, respectively (HR 4.67, CI [1.02 -21.4], p = 0.047; HR 2.48, CI [1.17-5.23], p = 0.02).Fig 1: Cumulative Incidence of Infection 6 Months Post CAR T-cell Therapy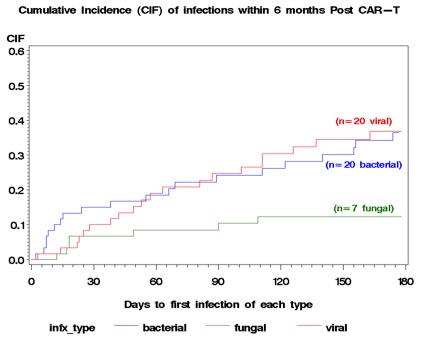
Conclusion:
Infections after CTT are common. Infection before CTT was associated with risk of infection after CTT. Pt selection may ameliorate this risk. Mortality due to fungal infections was high. Randomized-controlled trials of antifungal prophylaxis in high-risk pts are needed.

