22 - Patient Satisfaction Remains Unchanged Following Implementation of an Antibiotic Stewardship Intervention in Primary Care
Background:
Inappropriate prescription of antibiotics for respiratory tract infections (RTIs) in ambulatory care settings is common, increasing the risk of adverse health outcomes. Behavioral and educational interventions targeting primary care providers (PCPs) have shown promise in reducing inappropriate antibiotic prescribing for RTIs. While one perceived barrier to such interventions is the concern that these adversely impact patient satisfaction, few data exist in this area. Here, we examine whether a recent PCP-targeted intervention that significantly reduced antibiotic prescribing for RTIs was associated with a change in patient satisfaction.
Methods:
The PCP-targeted intervention involved monthly education sessions and peer benchmarking reports delivered to 31 clinics within an academic health system, and was previously shown to reduce antibiotic prescribing. Here, we performed a retrospective, secondary analysis of Press Ganey (PG) surveys associated with the outpatient encounters in the pre- and post-intervention periods. We evaluated the impact on patient perceptions of PCPs based on provider exposure to the intervention using a mixed effects logistic regression model.
Results: There were 17,416 out of 197,744 encounters (8.8%) with associated PG surveys for the study time period (July 2016 to September 2018). In the multivariate model, patient satisfaction with PCPs was most strongly associated with patient-level characteristics (age, race, health status, education status) and survey-level characteristics (survey response time, patient’s usual provider) (Figure 1). Satisfaction with PCPs did not change following delivery of the provider-based intervention even after adjusting for patient- and survey-level characteristics [adjusted odds ratio (95% CI): 1.005 (0.928, 1.087)]. However, a small increase in satisfaction associated with receiving antibiotics during the entire study period was seen [adjusted odds ratio (95% CI): 1.146 (1.06, 1.244)].Figure 1: Association of a provider-targeted intervention as well as patient, provider, and practice characteristics with patient satisfaction in a multivariable mixed effects logistic regression model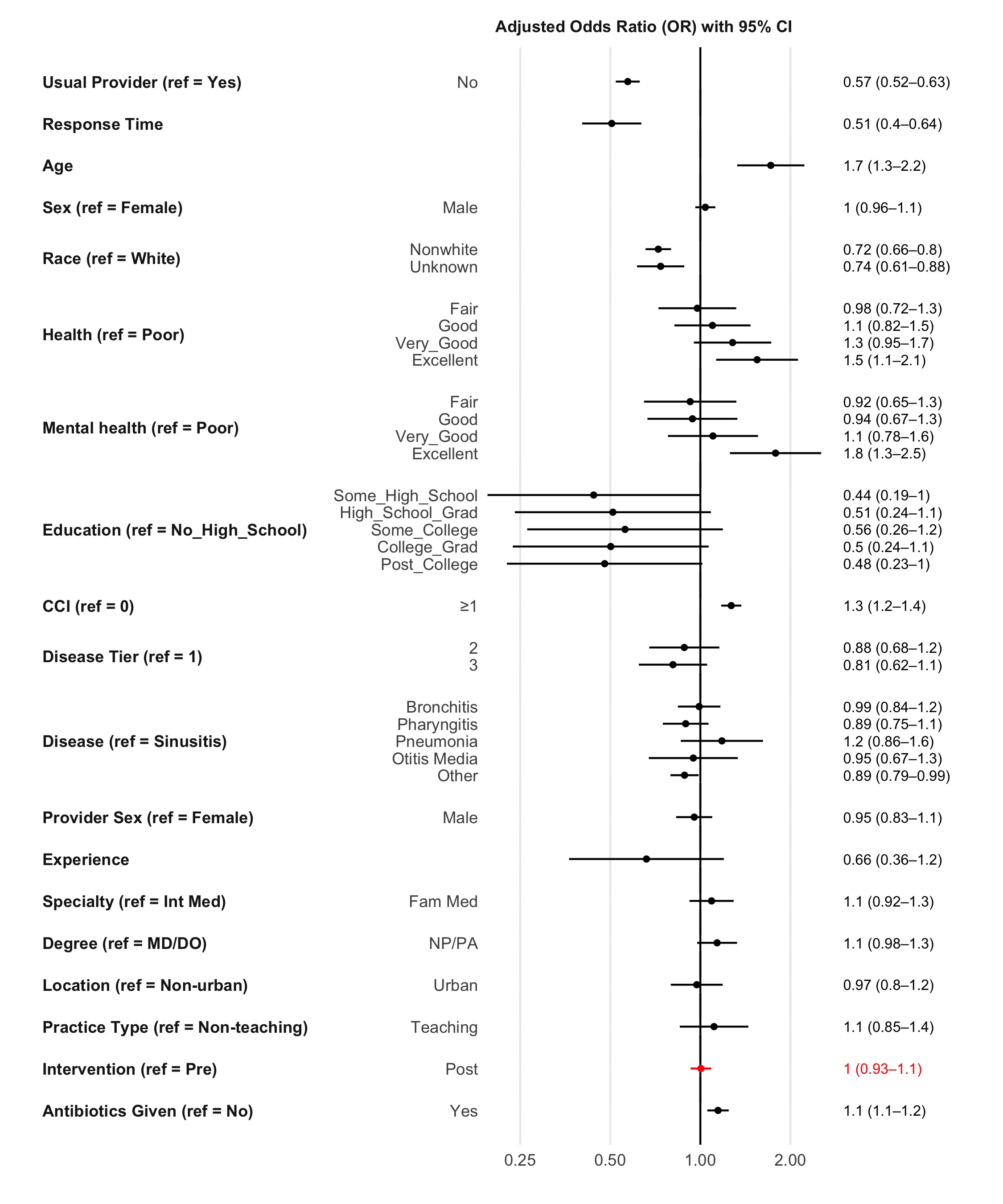
Conclusion:
Patient perceptions of PCPs remain unchanged following the delivery of a behavioral and educational intervention to primary care providers that resulted in observable decreases in antibiotic prescribing practices for RTIs.

Zachary Hostetler, MD, PhD
Internal Medicine Resident
Weill Cornell Medical College
New York, NYDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- KH
Keith W. Hamilton, MD
Associate Professor Of Clinical Medicine
Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, PADisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- LC
Leigh Cressman, MA
Biostatistician
University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine
Philadelphia, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- MT
McWelling H. Todman, MS (expected 2021)
Senior Analyst
Penn Medicine: University of Pennsylvania Health System
Philadelphia, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.

Ebbing Lautenbach, MD, MPH, MSCE
Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology
University of Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- LD
Lauren Dutcher, MD
Instructor of Medicine
University of Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, PennsylvaniaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.


