Category: Clinical Practice Issues
Poster Session: Clinical Practice Issues
593 - Additional medical expenditures attributable to pneumococcal disease in Japan
- HF
Haruhisa Fukuda
Associate Professor
Kyushu University
Fukuoka, Fukuoka, JapanDisclosure: Pfizer Japan Inc. (Scientific Research Study Investigator)
Presenting Author(s)
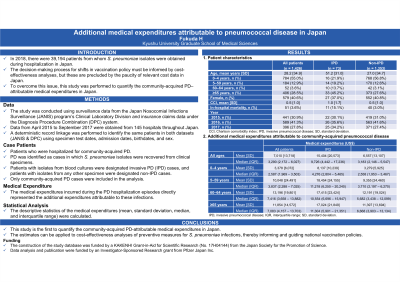
Background: Japan requires a reexamination of its current vaccination policies to reduce the prevalence of pneumococcal disease (PD). Although the decision-making process for vaccination programs must be informed by cost-effectiveness analyses, the lack of cost data from Japan precludes such investigations. This study was therefore performed to quantify the medical expenditures attributable to PD in Japan.
Methods: The study was conducted using surveillance data from the Japan Nosocomial Infections Surveillance (JANIS) program’s Clinical Laboratory Division and insurance claims data under the Diagnosis Procedure Combination (DPC) system. Data from April 2015 to September 2017 were obtained from 145 hospitals throughout Japan. As the analysis focused on community-acquired infections, the medical expenditures incurred during the PD hospitalization episodes directly represented the additional expenditures attributable to these infections. The descriptive statistics of the medical expenditures (mean, standard deviation, median, and interquartile range) incurred by the PD cases were calculated from the linked JANIS data and DPC data. In addition, these descriptive statistics were also generated according to the presence/absence of IPD and age groups.
Results: The study sample comprised 1,689 PD cases from 29 hospitals during the study period. Of these, 77 were IPD cases and 1,612 were non-IPD cases. The mean medical expenditures (standard deviation) for all PD cases, IPD cases, and non-IPD cases were estimated to be 1,016,801 yen (1,704,067 yen), 1,660,477 yen (2,078,667 yen), and 986,055 yen (1,678,705 yen), respectively. In addition, the medical expenditures associated with patients aged 60–64 years (1,646,739 yen) and 65 years or older (1,646,286 yen) were substantially higher than those of younger patients aged 5–59 years (1,424,105 yen).
Conclusion: These estimates have applications in cost-effectiveness analyses of PD preventive measures, which can subsequently inform and guide national vaccination policies.

