Category: Bacteremia
Poster Session: Bacteremia
299 - Paediatric Collaborative Network on Infections in Canada (PICNIC) Study of the Current Landscape of Gram Negative Bacteremias
- AL
Alice X. Lu
cMD
McMaster University
Hamilton, Ontario, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- KT
Kara Tsang
Ms.
McMaster University
Toronto, Ontario, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- MB
Michelle Barton
Pediatric Infectious Diseases Specialist
Children’s Hospital at London Health Centre
London, ON, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- CF
Craig Frankel
Dr Craig Frankel
Western University
London, Ontario, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- JM
Jane McDonald
Pediatric Infectious Diseases Specialist
Montreal Children's Hospital
Montreal, QC, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- JB
Jennifer Bowes
Research Coordinator
Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario
Ottawa, ON, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- JG
John Gunawan
Dr John Gunawan
University of Alberta
Edmonton, Alberta, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- SF
Sergio Fanella
Associate Professor
University of Manitoba
Winnipeg, MB, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- MA
Mohammad Alghounaim
Pediatric ID specialist and medical microbiologist
Department of Pediatrics, Amiri Hospital, Ministry of Health, Kuwait
Kuwait City, Al Asimah, KuwaitDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- JC
Jeannette Coumeau
Dr J Comeau
Dalhousie University
Halifax, Nova Scotia, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- KL
Kirk Leifso
Dr Kirk Leifso
Queen's University
Kingston, Ontario, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- RS
Robert Slinger
Pediatric Infectious Diseases Specialist
Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario
Ottawa, Ontario, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- JR
Joan Robinson
Pediatric Infectious Diseases Specialist
Stollery Children's Hospital
Edmonton, AB, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
- SK
Sarah Khan
Assistant Professor, Associate Medical Director Infection Prevention and Control
McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Hamilton, Ontario, CanadaDisclosure: I do not have any relevant financial / non-financial relationships with any proprietary interests.
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Background: Antimicrobial resistance is a public health threat, invasive infection from multi-drug resistant gram-negative (MDRGN) pathogens is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The incidence of MDRGN bacteremia in Canada is rising, and pediatric data is limited.
Methods: This retrospective chart review of paediatric patients with gram negative bacteremia in a multicenter PICNIC database (n=7 centers) from 2013 to 2017. MDRGN was defined as enterobacteriaceae that were resistant to third generation cephalosporins (including ESBL, CPE). Ethics approval was obtained at all sites, and data was entered into a secure REDCAP database, descriptive statistics are described herein.
Results:
Of the 676 bacteremia patients in the database, 214 (31.7%) were gram negative pathogens. E. coli was the most frequent pathogen (59.8%, of which 22 of 128 were MDR), followed by Klebsiella (31.8%, of which 9 of 68 were MDR). Of the 31 MDRGNs, 19 were ESBL, 1 was a CPE, and 11 were nonspecific mechanisms of resistance. There were no multidrug resistant Pseudomonas, Stenotrophomonas, or Acinetobacter. The majority of patient were less than 3 months of age (59.3%) and were male (58.8%). The majority had an underlying comorbid condition; hematoncologic diagnosis accounting for 14.5%. Length of stay varied from 1 to 742 days (mean 72, standard deviation 88). 11% required admission to ICU, 10% required removal of a intravascular catheter, 7% required a change in ventilation status, 2% requiring procedural source control, and there was an 8% mortality rate. Treatment duration greater than 14 days occurred in 123 patients (61% of patients).Table 1. Demographic and clinical data of cases.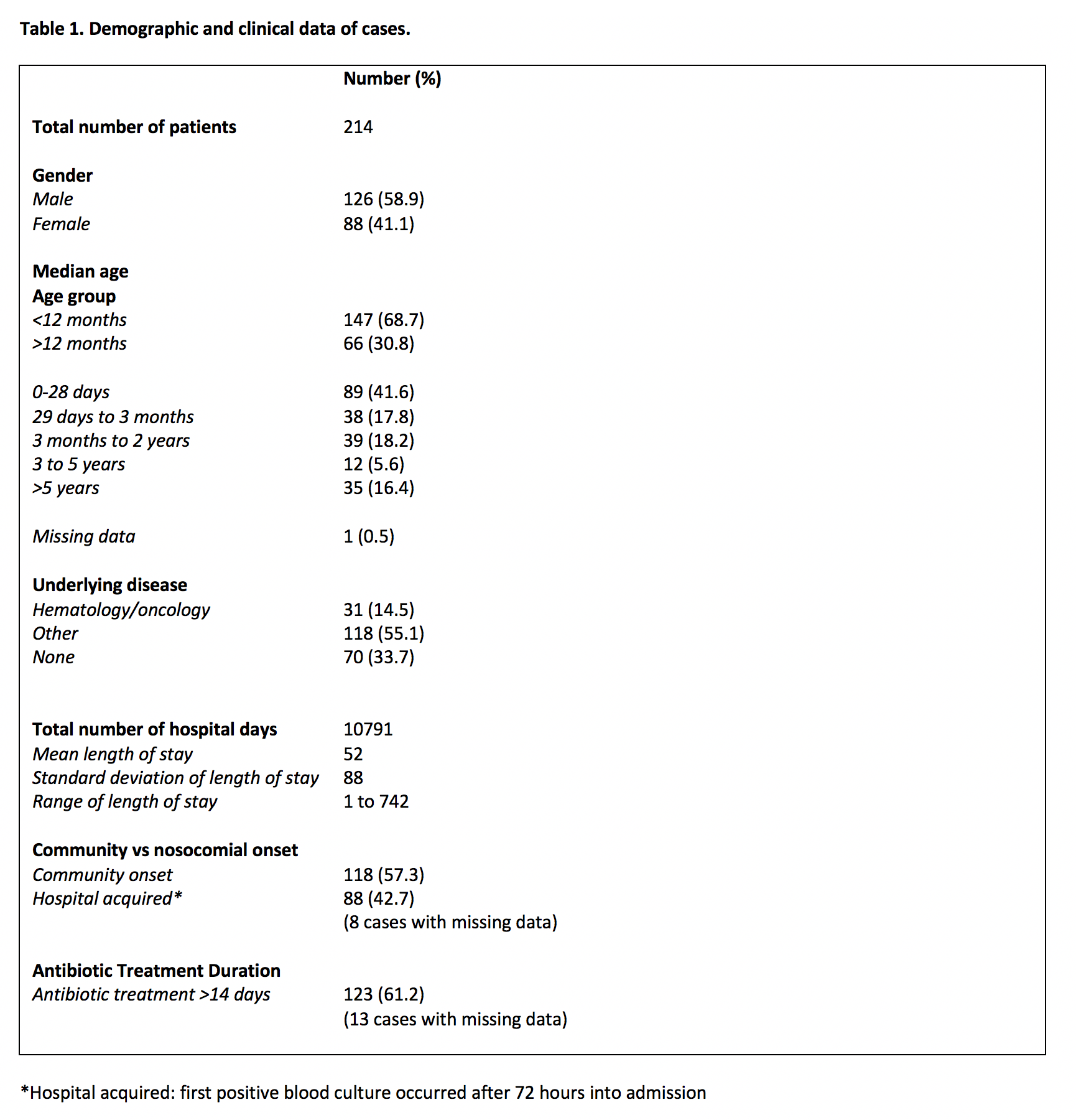 Table 2. Isolated species and patterns of resistance.
Table 2. Isolated species and patterns of resistance..png) Table 3. Complications in treatment due to infection.
Table 3. Complications in treatment due to infection..png)
Conclusion: This preliminary analysis of a multicenter review of pediatric gram negative bacteremias demonstrates a higher risk in neonates with comorbid conditions. A surprisingly prolonged treatment duration of greater than 14 days occurred in the majority of patients. Further analysis to assess factors associated with prolonged treatment durations, MDR infection, and complications is required. Gram negative bacteremia remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in pediatric patients.

